Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) antigen
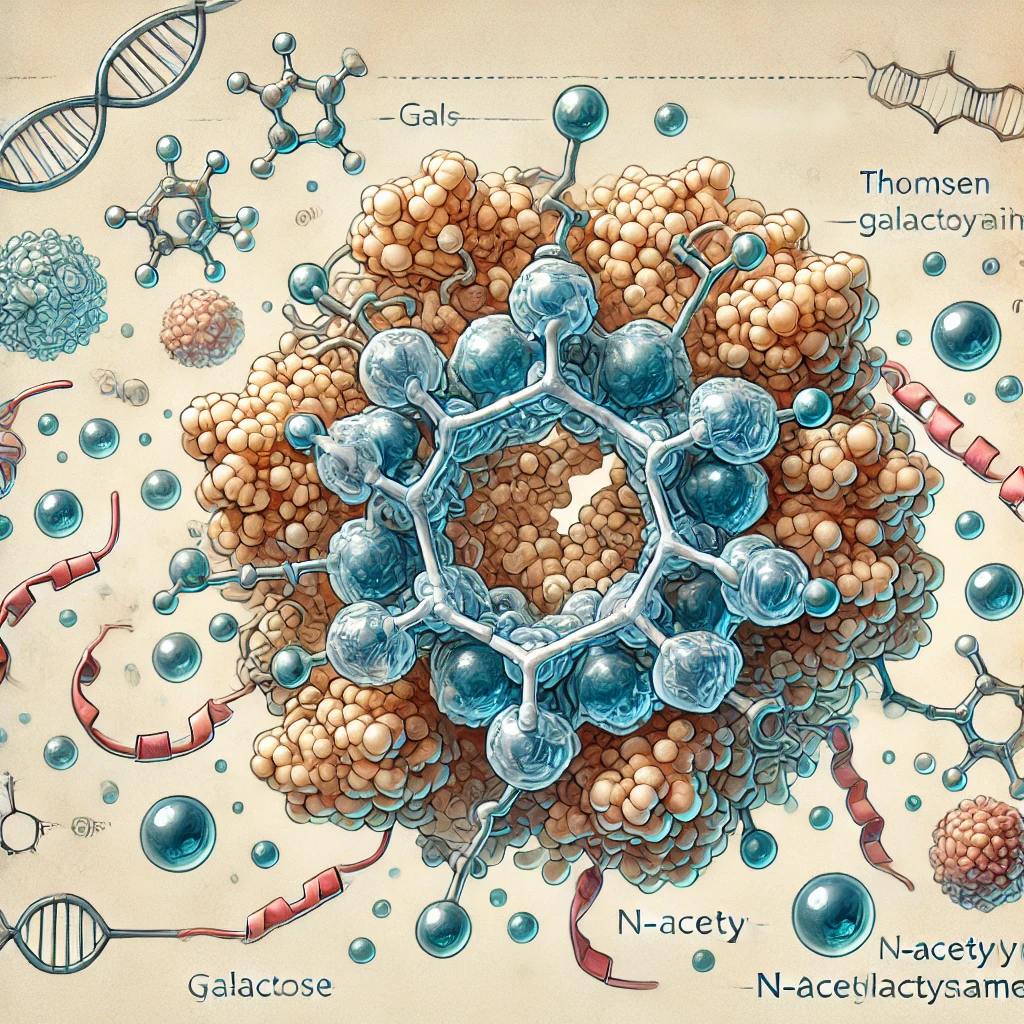
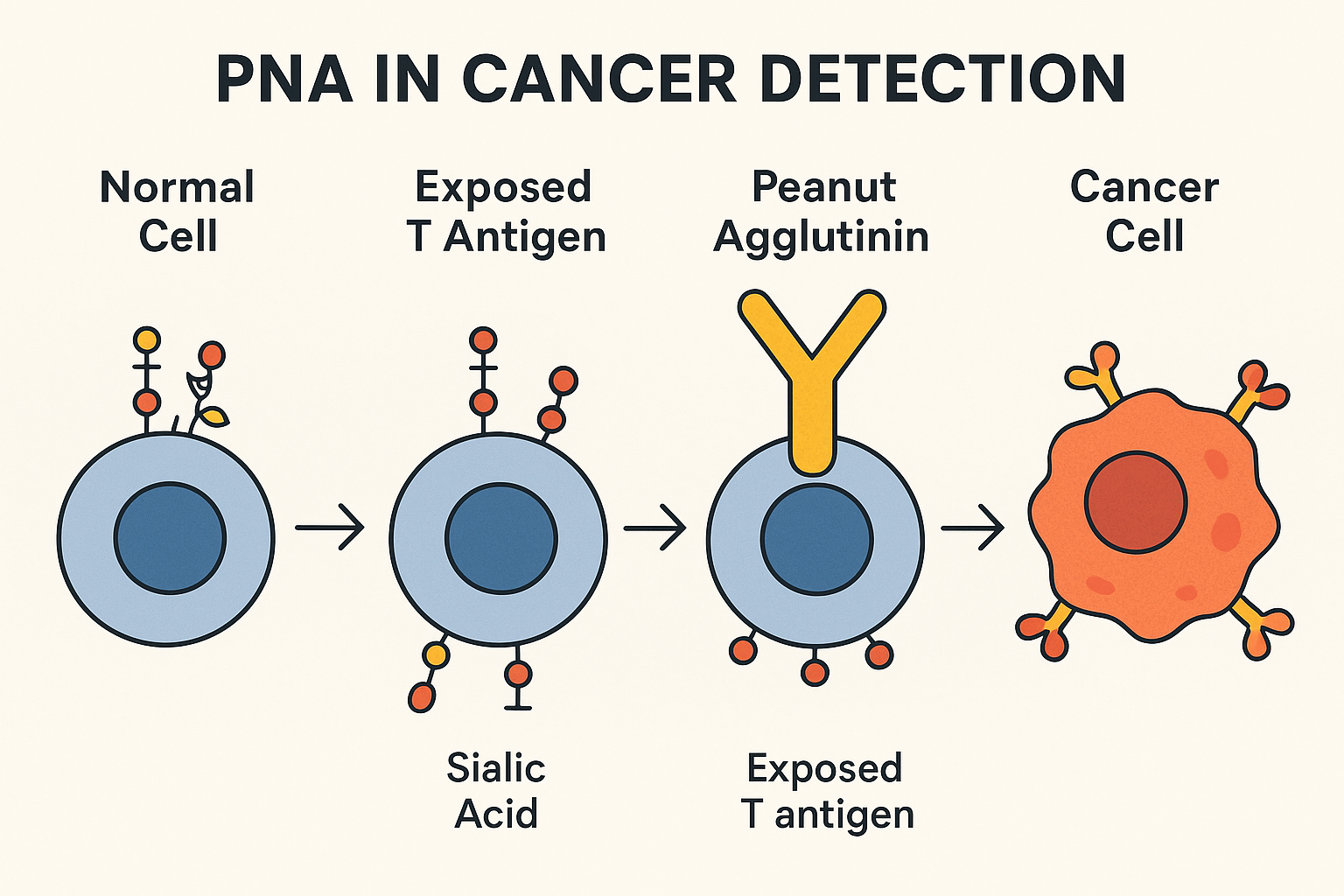
The Thomsen–Friedenreich (TF) antigen, also known as CD176, is a disaccharide structure comprising galactose and N-acetylgalactosamine (Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-Ser/Thr). It serves as the core 1 structure in O-linked glycosylation of proteins. In healthy tissues, the TF antigen is typically masked by additional carbohydrate chains or sialylation, rendering it inaccessible to the immune system. However, in many cancer cells, aberrant glycosylation leads to the unmasking and overexpression of the TF antigen on the cell surface. This unmasking is observed in up to 90% of carcinomas and certain leukemias, making the TF antigen a significant oncofetal marker associated with tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance
Key Aspects of TF Antigen Documentation
- Discovery & Structure:
- The TF antigen, also known as T antigen or Galβ1-3GalNAc, is a disaccharide structure that is normally masked by other glycan residues on glycoproteins in most healthy tissues.
- It is exposed and becomes unmasked in various cancers, making it a significant marker in tumor detection.
- Presence in Cancer:
- The TF antigen is overexpressed in several types of cancer, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, and lung cancer. Its exposure is associated with tumorigenesis, metastasis, and tumor progression.
- It has been documented as part of the mucin glycoprotein family, especially in mucin-like glycoproteins (e.g., MUC1), which are heavily glycosylated and present in various cancers.
- Role in Tumor Biology:
- TF antigen is thought to be involved in cell adhesion, immune evasion, and tumor cell migration, all of which contribute to metastatic spread.
- Studies show that the TF antigen may shield tumor cells from immune surveillance, helping them avoid detection by the body’s immune system.
- Detection Methods:
- Lectins like peanut agglutinin (PNA) specifically bind to the TF antigen, and monoclonal antibodies targeting the TF antigen have been developed for use in diagnostic tests, including immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry.
- It is also being investigated as a potential target for immunotherapy and cancer vaccines.
- Research Applications:
- Over the years, there has been a significant amount of research on TF antigen as a biomarker for early cancer detection and monitoring treatment responses.
- Several studies have confirmed that TF antigen plays a key role in tumor progression and is documented as a relevant target for early diagnostics.
Research Highlights:
- Overexpression in Cancers: Numerous studies document the high expression of TF antigen in malignant tumors, leading to its investigation as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker.
- Therapeutic Target: TF antigen is being explored for its potential use in targeted therapies, such as monoclonal antibody treatments or vaccine development aimed at inducing an immune response specifically against tumor cells expressing the antigen.
Key References:
- Cancer Research: Studies showing TF antigen as a key factor in cancer progression and its ability to serve as a diagnostic biomarker.
- Immunotherapy: Exploration of anti-TF monoclonal antibodies to boost immune system recognition of tumor cells.
- Diagnostic Applications: TF antigen detection methods using lectins and antibodies for potential diagnostic applications.
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Thomsen-Friedenreich-Antigen
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1810470/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thomsen%E2%80%93Friedenreich_antigen
In summary, Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen is not only well-documented but is also an important target in cancer research and diagnostics, with ongoing studies aimed at harnessing its potential in early detection and therapeutic intervention.
#ThomsenFriedenreichantigen #TFantigen #cancerresearch #galactoseN-acetylgalactosamine