Causes of High Alpha Fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein normally produced by the fetal liver and yolk sac during development. In adults, AFP levels are usually very low, so an elevated AFP can be a sign of certain medical conditions. Causes include:
1. Liver-related conditions
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) – primary liver cancer; one of the most common causes of markedly elevated AFP.
- Chronic liver diseases – such as hepatitis B or C infection, alcoholic liver disease, and cirrhosis (AFP may be mildly elevated due to regeneration of liver cells).
- Liver metastases – secondary tumors in the liver can sometimes cause increases.
2. Germ cell tumors
- Non-seminomatous testicular cancer – especially yolk sac tumors and embryonal carcinoma.
- Ovarian germ cell tumors – yolk sac tumors (endodermal sinus tumors) can produce high AFP.
- Extragonadal germ cell tumors – in locations like the mediastinum or retroperitoneum.
3. Pregnancy-related causes
- Normal pregnancy – AFP is naturally elevated, peaks in the 2nd trimester.
- Pregnancy complications – such as neural tube defects (spina bifida, anencephaly), abdominal wall defects (gastroschisis, omphalocele), or fetal demise.
4. Other less common causes
- Hereditary persistence of AFP – a benign genetic trait where AFP remains mildly elevated lifelong.
- Ataxia-telangiectasia – rare inherited disorder.
- Other malignancies – stomach, pancreas, or lung cancers (rarely).
Key points:
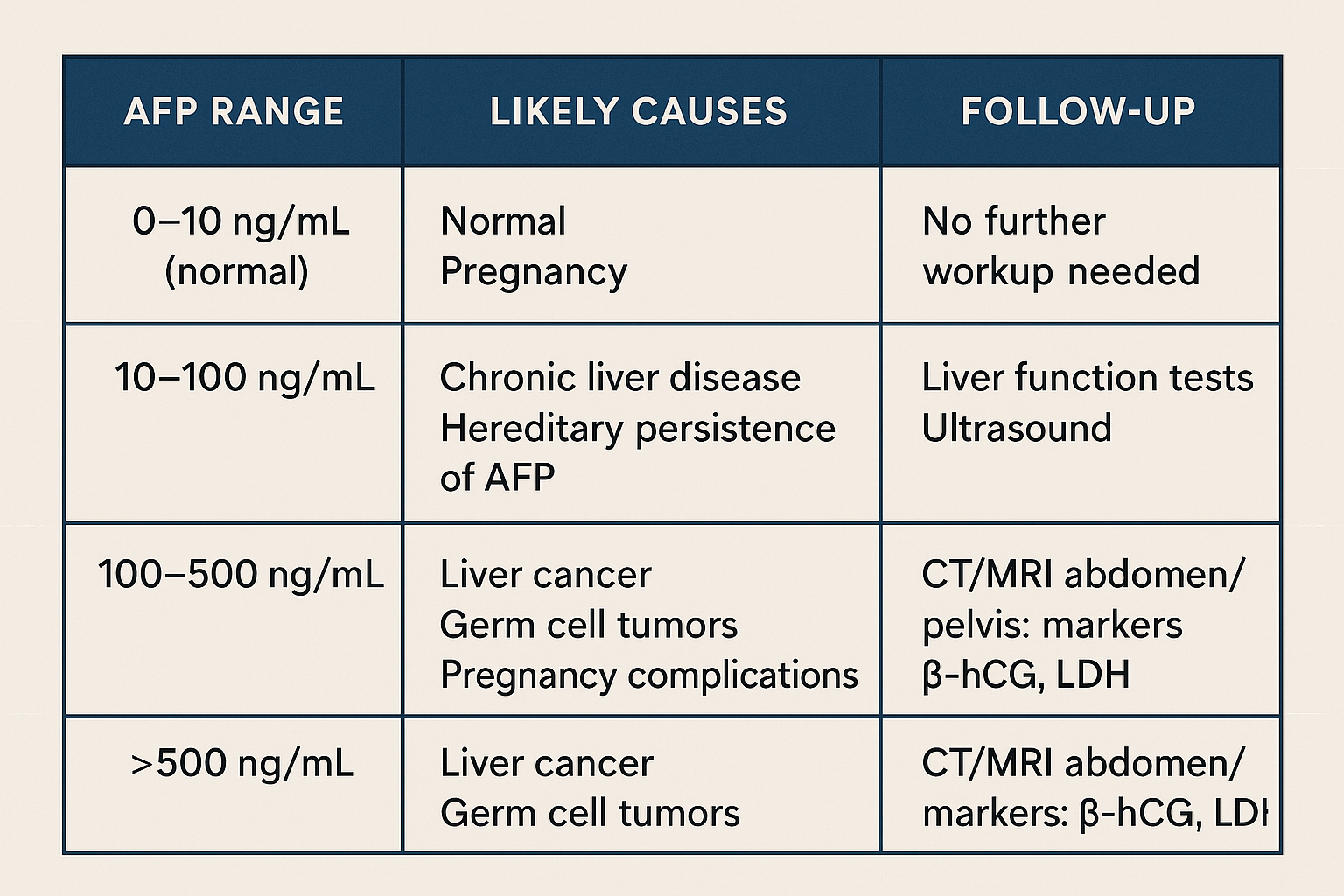
- Mild elevations (just above normal) are often due to chronic liver disease or benign conditions.
- Markedly high levels (hundreds to thousands of ng/mL) are more suspicious for cancer, especially HCC or germ cell tumors.
- AFP is not perfectly specific — results should always be interpreted alongside imaging, other tumor markers (like β-hCG, LDH), and clinical findings.
Important Notes
- AFP levels alone are not diagnostic. They must be interpreted alongside imaging, biopsy, and other lab results.
- In patients with chronic liver disease, an AFP level above 200 ng/mL may strongly suggest liver cancer2.
- The AFP-L3% test can help differentiate benign liver conditions from malignant ones.
#CausesofHighAlphaFetoprotein